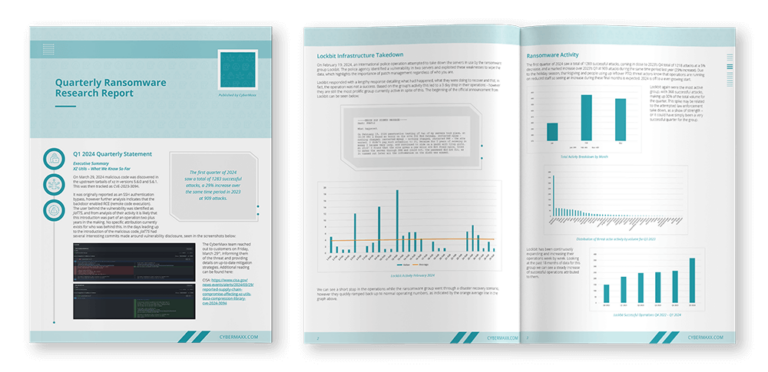
Cybersecurity compliance in 2024 will add new pressures to businesses. It includes updated security measure requirements and rules for managing customer data. Failure to stay current on this year’s regulatory demands could bring hefty fines and a higher risk of cyber incidents.
Overview: Cybersecurity Compliance 2024
Everyone in cybersecurity understands the role compliance plays in their day-to-day. It adds costs for adhering to the requirements and piles stress and worry that you’re within the guidelines. Current federal regulations are too many to count — we’ll just name the big ones:
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for securing patient information
- Federal Trade Commission Act (FTCA) that sets data security and consumer privacy requirements for businesses
- The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to set security standards that protect European Union (EU) residents
- Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation (DFAR) for setting baseline standards for DoD contractors
- Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA) that has minimum security standards for federal agencies
These don’t even include industry-set guidelines. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), for example, has requirements for anyone processing credit card data. Nevertheless, we also can’t forget the current landscape of state compliance:
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) for ensuring privacy and data transparency for state residents
- New York State Department of Financial Services (NYDFS) for protecting systems in the New York finance industry
- Colorado Privacy Act (CPA) to maintain consumer privacy within the state
- Connecticut Data Privacy Act (CTDPA) for ensuring resident privacy and online security
- Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA) to maintain security thresholds for resident data
Adhering to these state and federal regulations is not optional. Fines and a diminished brand reputation await anyone who chooses ignorance.
Anticipated Changes in Federal Security Regulations
We’ve already seen 2024 updates in federal security compliance. For example, the Security Exchange Commission (SEC) recently set requirements that went into effect for publicly traded companies. It includes reporting standards for security program management and governance, plus disclosure requirements for cyber incidents.
Others we expect for 2024:
- Activation of Cybersecurity Resilience Act (CRA): Sets requirements for hardware and software sold in the EU
- Updates to the Kids Online Safety Act: Enacts more measures for protecting children’s online safety and privacy
- Provisions to HIPAA: Adds new requirements for exchanging and information sharing amongst healthcare providers
If the pattern continues, we could also see other federal rules enacted (though not necessarily in effect) for the FTC, Cybersecurity Infrastructure and Security Agency (CISA), and Department of Homeland Security. These could be requirements for security controls, consumer privacy management, or intelligence sharing.
What’s this all mean for you? Time and money spent learning the new requirements for your business. It’ll also demand new investments in compliance management activity so you don’t fall short of the guidelines.
Anticipated Changes in State Cybersecurity Regulations
Over the last few years, many states have sought to replicate CCPA for resident data protection. In 2024, five more U.S states will have security and privacy requirements go into effect:
- Florida Digital Bill of Rights (FDBR)
- Texas Data Privacy and Security Act(TDPSA)
- Oregon Consumer Privacy Act (OCPA)
- Montana Consumer Data Privacy Act (MTCDPA)
- Utah Consumer Privacy Act (UCPA)
Similarly, others have declared requirements that will begin in 2025 and 2026. We can also assume states without regulations will, at a minimum, start having conversations for future compliance. Child social media laws are also a hot topic of conversation — specifically regarding data protection from ads and brokers.
2024 will also see updates to NYDFS. For example, new security governance, risk assessment, and policy management measures for financial services companies.
State regulations get tricky because of the variance between each state’s laws. It’s also tough to decipher the overlap between federal and state laws. For example, HIPAA, a federal law, looks different in California compared to Virginia regarding HIPAA exceptions and whether it applies to patient data, healthcare entities, or both.
Regardless, companies operating in multiple states must consider clashing laws in their compliance and cybersecurity programs.
Preparing for 2024 Compliance: Strategies for Businesses
Proactiveness is vital to preparing for anticipated compliance changes in 2024. Governing bodies usually write federal and state cybersecurity laws a few years before they go into effect. So, take advantage of the gap period to:
- Understand the new or updated requirements
- Conduct a gap analysis to evaluate current controls compared to regulatory standards
- Get a plan of action to adopt new security measures before the activation date
Internal audits should also be a regular activity. Check to ensure policies and procedures align with what’s required. For many regulations, you’ll need written documentation for plans like program management, incident response, and stakeholder notification for breaches.
Finally, don’t handle compliance on your own. Managing cybersecurity is stressful enough. And nuanced legal and technical complexities only add more headaches. Partner with a governance, risk, and compliance specialist who can take this burden off your plate.
Managing Cybersecurity Compliance in 2024
Adhering to federal and state cybersecurity laws in 2024 is a non-negotiable. Complying with the updates helps to avoid legal issues and hefty penalties. It’ll keep you within the security guardrails — providing a competitive advantage in today’s evolving cyber threat landscape.